Services / 2D Imaging
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipiscing elit sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua
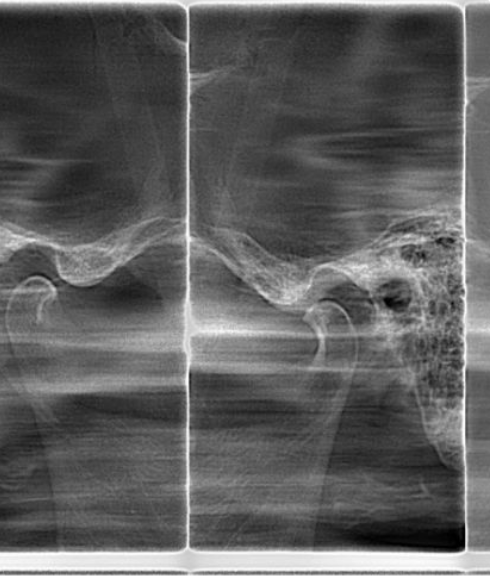
2D TMJ
The TMJ is a freely movable articulation between the condyle of the mandible and the squamous portion of the temporal bone at the base of the skull. The bilateral articulation of the mandible to the cranium Implies that the left and right TMJs must act as a single unit. Physical examination alone is inaccurate in determining the status of the joint. The primary rationale for imaging the TMJ lies in the fact that mechanical internal derangement is treated differently from the multiple miscellaneous disorders. The TMJ is a freely movable articulation between the condyle of the mandible and the squamous portion of the temporal bone at the base of the skull. The bilateral articulation of the mandible to the cranium Implies that the left and right TMJs
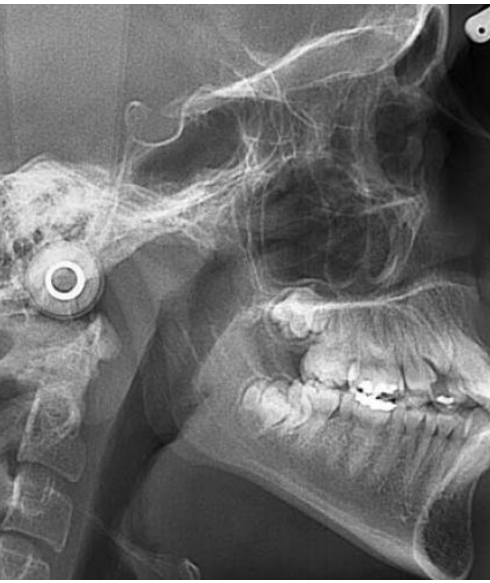
Cephalometric
The TMJ is a freely movable articulation between the condyle of the mandible and the squamous portion of the temporal bone at the base of the skull. The bilateral articulation of the mandible to the cranium Implies that the left and right TMJs must act as a single unit. Physical examination alone is inaccurate in determining the status of the joint. The primary rationale for imaging the TMJ lies in the fact that mechanical internal derangement is treated differently from the multiple miscellaneous disorders. The TMJ is a freely movable articulation between the condyle of the mandible and the squamous portion of the temporal bone at the base of the skull. The bilateral articulation of the mandible to the cranium Implies that the left and right TMJs
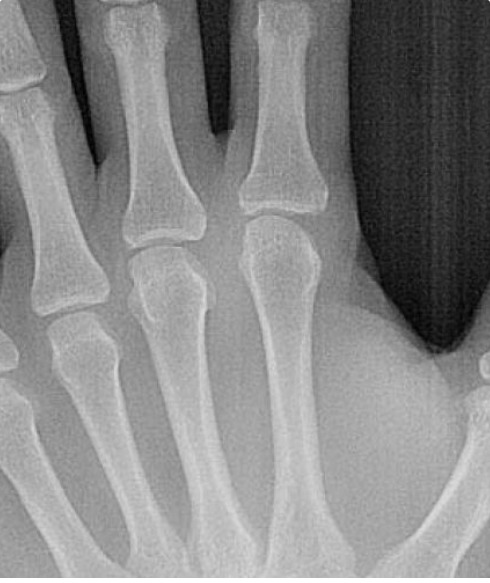
Hand Exposure
The TMJ is a freely movable articulation between the condyle of the mandible and the squamous portion of the temporal bone at the base of the skull. The bilateral articulation of the mandible to the cranium Implies that the left and right TMJs must act as a single unit. Physical examination alone is inaccurate in determining the status of the joint. The primary rationale for imaging the TMJ lies in the fact that mechanical internal derangement is treated differently from the multiple miscellaneous disorders. The TMJ is a freely movable articulation between the condyle of the mandible and the squamous portion of the temporal bone at the base of the skull. The bilateral articulation of the mandible to the cranium Implies that the left and right TMJs
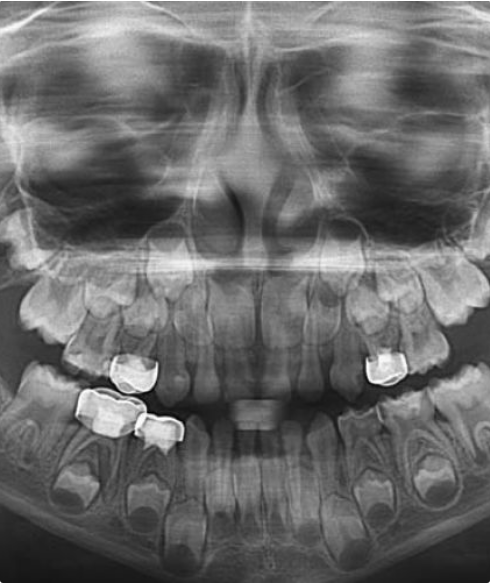
Panorama
The TMJ is a freely movable articulation between the condyle of the mandible and the squamous portion of the temporal bone at the base of the skull. The bilateral articulation of the mandible to the cranium Implies that the left and right TMJs must act as a single unit. Physical examination alone is inaccurate in determining the status of the joint. The primary rationale for imaging the TMJ lies in the fact that mechanical internal derangement is treated differently from the multiple miscellaneous disorders. The TMJ is a freely movable articulation between the condyle of the mandible and the squamous portion of the temporal bone at the base of the skull. The bilateral articulation of the mandible to the cranium Implies that the left and right TMJs